Ozone therapy is a set of techniques that use medical ozone as a therapeutic agent. Medical ozone is a mixture of a maximum of 5% ozone and 95% oxygen.
In 1885 Dr. Charles J. Kenworth wrote the first book on ozone as a medical therapy, and its use was greatly encouraged during World War I for cleaning and disinfecting wounds.
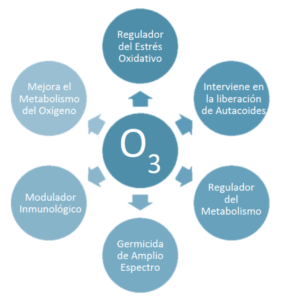
Ozone dissolves immediately in the body’s water, both in plasma and in extracellular fluids because its solubility is ten times greater than that of oxygen. Thanks to this ability, O3 reacts with biological substances with double or triple carbon-carbon bonds present in cells, fluids or tissues: proteins, amino acids, unsaturated fatty acids, DNA molecules, cysteine residues of proteins, plasma lipoprotein complexes and the double layer of cell membranes.
When it reacts with membrane phospholipids it produces:
- Ozonides
- Aldehydes
- Peroxides
In adequate and controlled quantities, these metabolites exert different biological and therapeutic functions, act as second messengers, chemical and immune response mediators, activate enzymes, etc…
Currently, different routes are used to administer ozone without toxic effects on the organism.
These means include rectal, vaginal, intramuscular, subcutaneous, intravenous or directly into the blood drawn from the patient through a process called autohemotherapy (major and minor).
Topical and oral administration of ozone can also be used on a daily basis, thanks to the stabilization of the O3 molecule in a source of vegetable fat or oil.
Do you want to know how these products work?